FHIR Structure
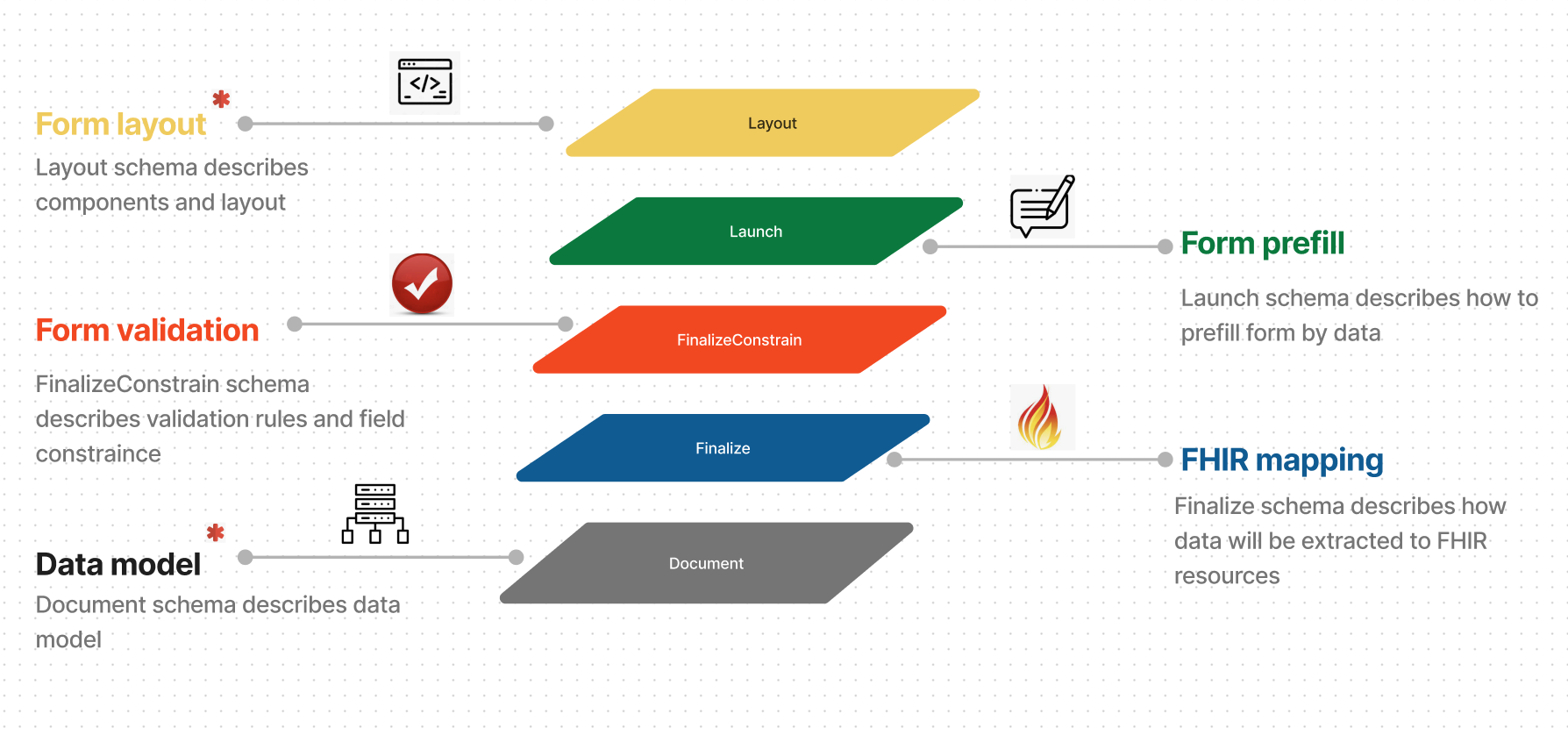
1. Form Layout
The form layout is the backbone of any form's user experience. This layout is driven by a layout schema that outlines the various components and their positions. Much like the blueprint of a building, the layout schema is essential for constructing the form's visual elements and the user's navigation through it. By using a schema, consistency and ease of modifications are ensured. Components might range from text fields, dropdowns, checkboxes, to more intricate widgets tailored for specific inputs. The layout isn't just about aesthetics; it plays a pivotal role in making the form user-friendly and intuitive.
2. Form Prefill
Entering repetitive data in a form can be a tedious task for users. This is where the Form Prefill comes into play. Leveraging a launch schema, it automates the process of filling in certain fields based on previously available data. Not only does this reduce redundancy but also minimizes human errors. This pre-filling can be particularly handy in forms where historical or session-specific data can be reused. The launch schema is a guidebook that determines which fields should be prefilled and from which data sources they should fetch the information.
3. Form Validation
A well-functioning form is not just about capturing data but ensuring that the captured data is accurate and adheres to certain rules. This is achieved through form validation. Using the finalize constrain schema, the form checks the input against a set of validation rules and field constraints. Whether it's ensuring an email is in the correct format, a mandatory field isn't skipped, or a number entered falls within a certain range, the validation process is crucial. This layer of validation ensures that the data collected is of high quality and ready for further processing or storage.
4. FHIR Mapping
With the healthcare domain evolving towards standardized data structures like FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), it's vital to align form data with these standards. The FHIR Mapping process, driven by the finalize schema, orchestrates how the collected data will be translated and stored as FHIR resources. This isn't just a matter of changing data format but often involves understanding intricate relationships between various healthcare data points. By defining how data will be extracted to FHIR resources, the system ensures interoperability and future-proofing in a constantly evolving healthcare IT landscape.
5. Data Model
Behind every form lies a robust data model that determines what kind of data will be stored and how it will be structured. This model is outlined by the document schema, serving as a skeleton for the data architecture. It describes the relationships between fields, acceptable data types, and other hierarchical or relational aspects of the data captured. Having a well-defined data model is essential for ensuring consistency, easing data retrieval, and setting the stage for scalable and sustainable data management in the future.